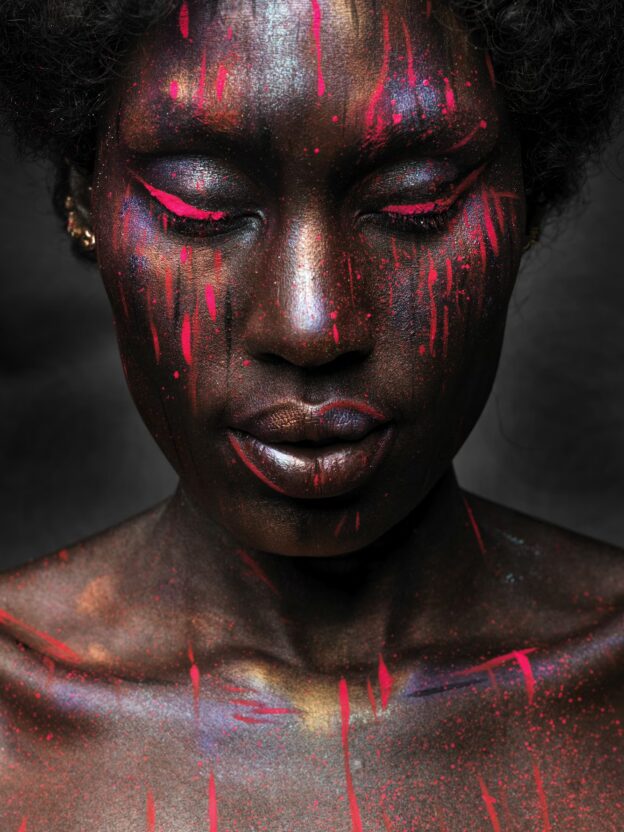
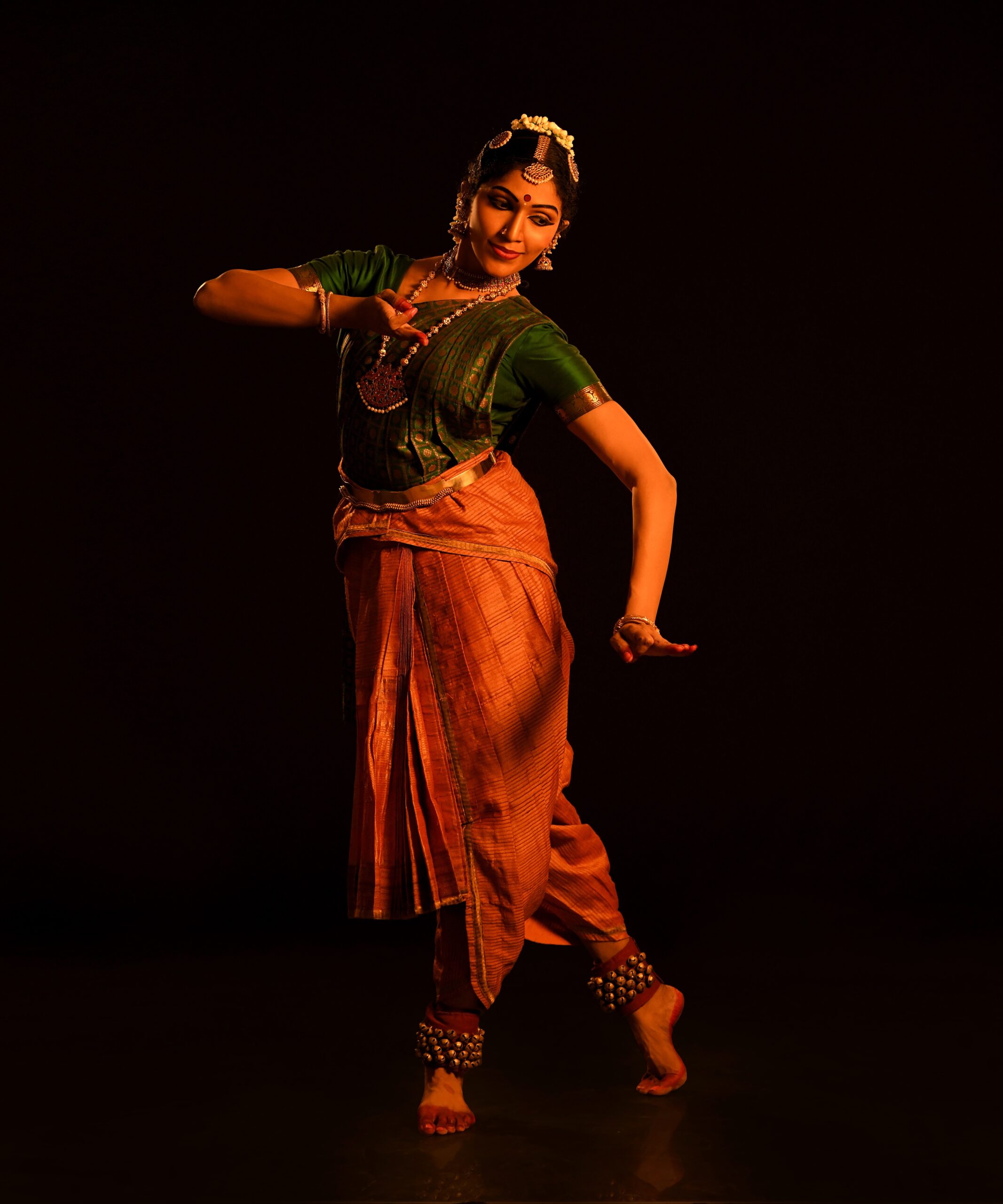
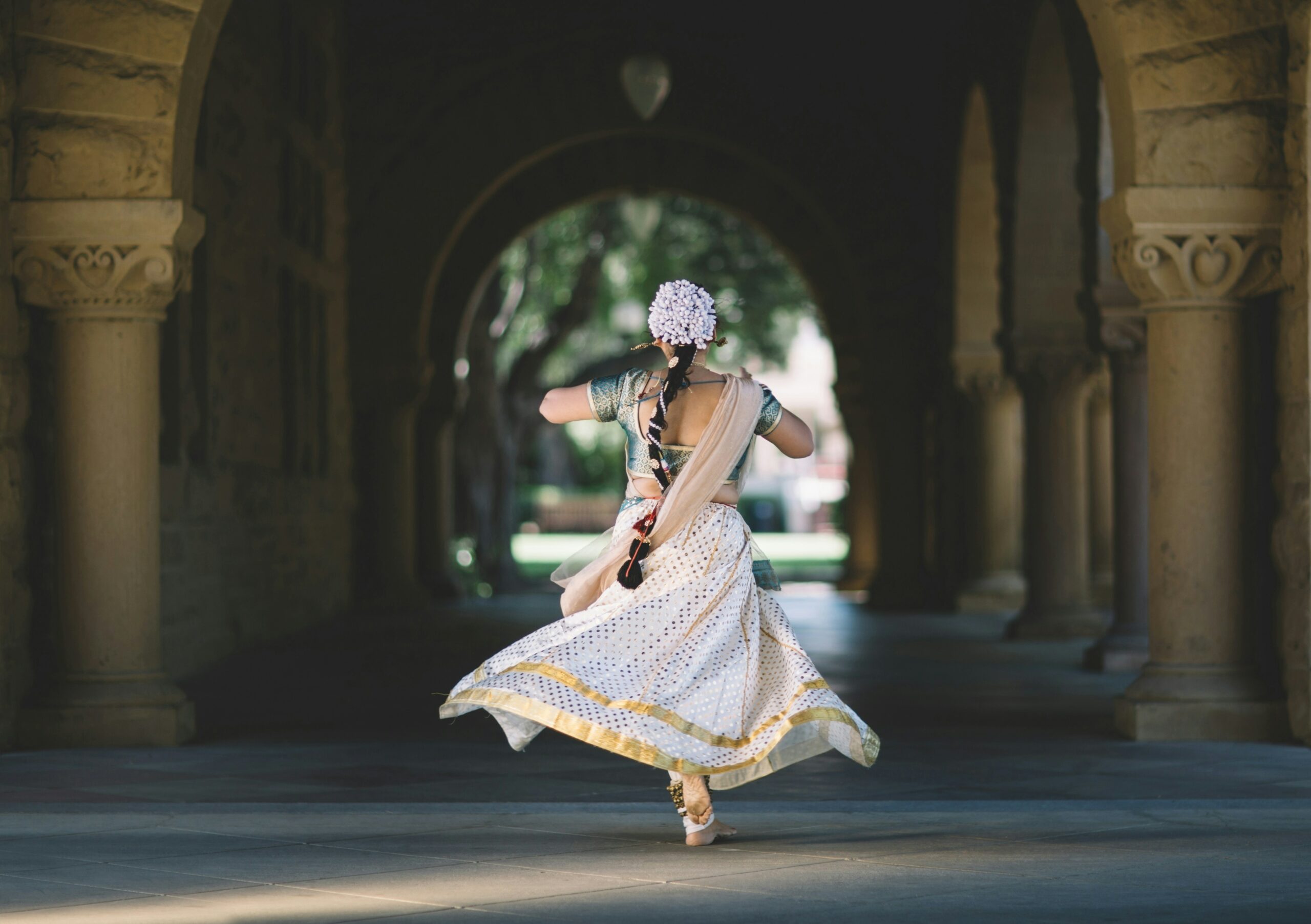
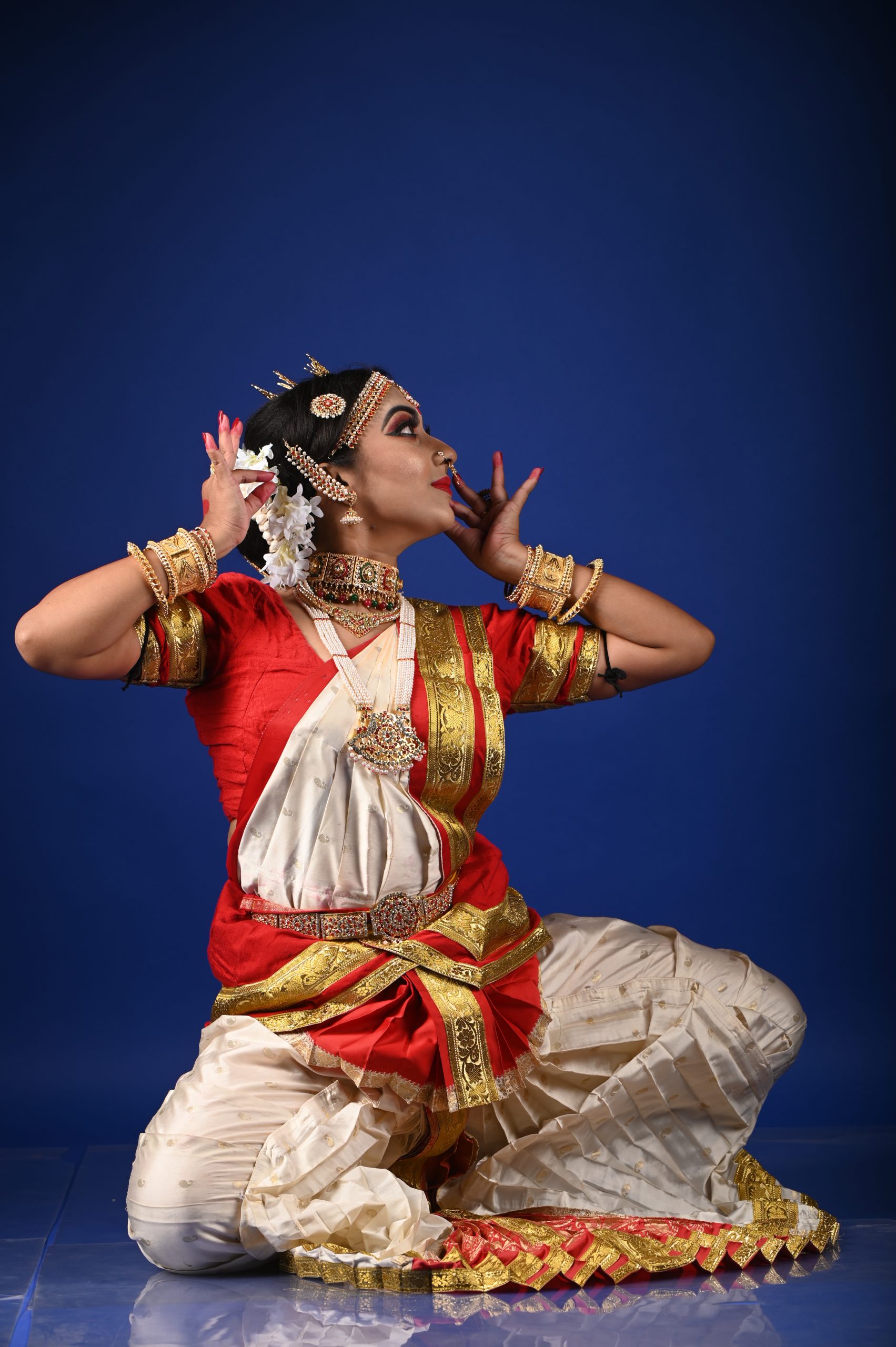
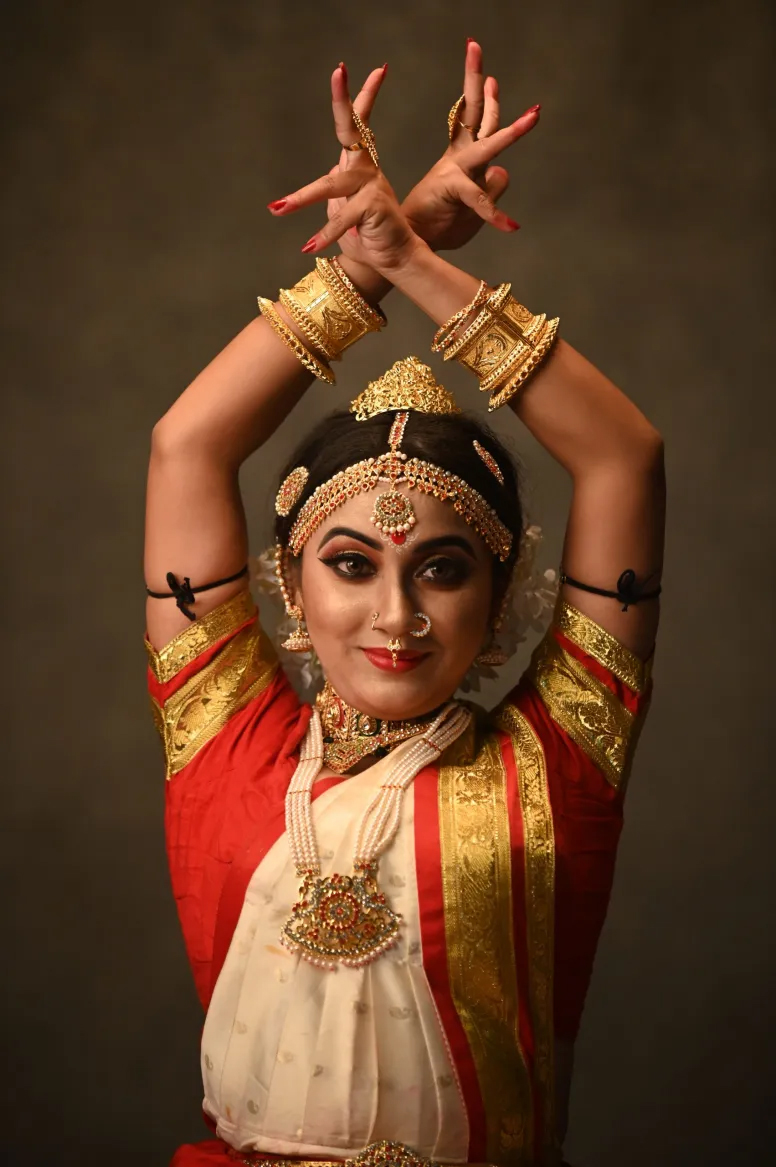
Fashion photography has the power to celebrate identity, culture, and beauty. Yet for decades, the industry often failed to light and photograph dark skin tones with the care and expertise they deserve. The problem never stemmed from dark skin, it came from photographers who were trained on narrow standards and equipment calibrated for lighter complexions. As the fashion world pushes for greater inclusion, the ability to photograph dark skin with accuracy and respect has become an essential skill. When done well, the results are striking. The richness of tone, depth, and texture creates images that command attention and honour the subject.
This article explores the techniques and sensitivities needed to capture dark skin beautifully, with a focus on practical lighting choices, exposure strategies, styling considerations, and the mindset that keeps the work respectful.
Understanding Light and How Skin Responds
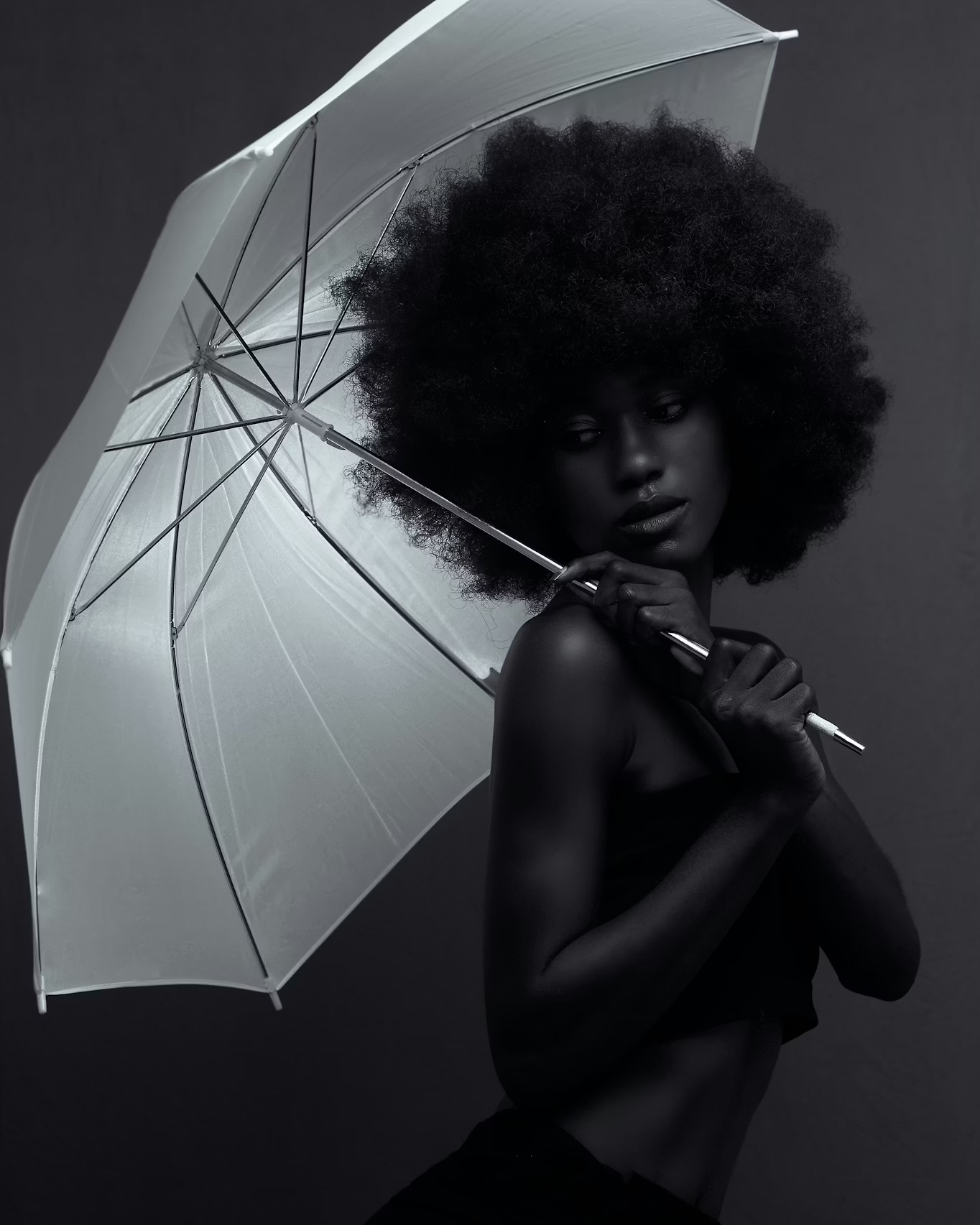

Dark skin absorbs more light than lighter skin. This means photographers must think more intentionally about how they shape and distribute their light. The goal is not to blast the subject with brightness. The goal is to reveal detail and dimension while keeping the natural richness of the skin intact.
Soft, diffused light is the strongest foundation. It wraps gently, avoids harsh falloff, and helps maintain depth. A large softbox, umbrella, or window source works well. When using harder light, it should be controlled with precision. Strong highlights can look beautiful on dark skin, but uncontrolled hotspots can flatten the shot.
Lighting ratios also matter. If the key light is too strong relative to the fill, the shadows can fall off too quickly. A balanced ratio preserves detail in the darker areas of the face. Photographers who understand this can create portraits that feel vibrant rather than muted.
Exposure: A Crucial Step
Many photographers make the mistake of overexposing dark skin in an effort to brighten it. This strips away the natural tone and removes the depth that makes the skin so compelling. Instead, the focus should be on achieving a clean exposure that brings out detail without washing out the subject.
Exposing for the highlights is a reliable approach. Dark skin often carries beautiful highlight areas along cheekbones, the forehead, and the bridge of the nose. If these highlights are preserved, the rest of the tones can be managed in post without distortion.
Tools like zebras and histograms help prevent clipping. Shooting in RAW provides even more flexibility. It allows the photographer to adjust shadows, contrast, and colour temperature with care. The idea is to respect the skin as it is, not to force it into a lighter or flatter version of itself.
Colour Balance and Skin Accuracy
White balance can either lift or dull dark skin. A slightly warmer balance often brings out radiance without changing the skin’s natural tone. Too much warmth, however, can make the subject appear artificially red or orange. The aim is nuance. Every face has its own balance of undertones. Photographers who take the time to understand these differences create images that feel true.
Avoiding heavy blue or green casts is important. They can create a grey or muddy effect that is difficult to correct. If shooting in mixed lighting environments, gel the lights or switch to a single consistent source. Clothing colours and backdrop tones should also be chosen with care. Colours like emerald, cobalt, burgundy, and gold often complement dark skin beautifully. Pale pastels can work if the lighting is strong enough to separate the subject from the background.
Highlights, Texture, and Shine
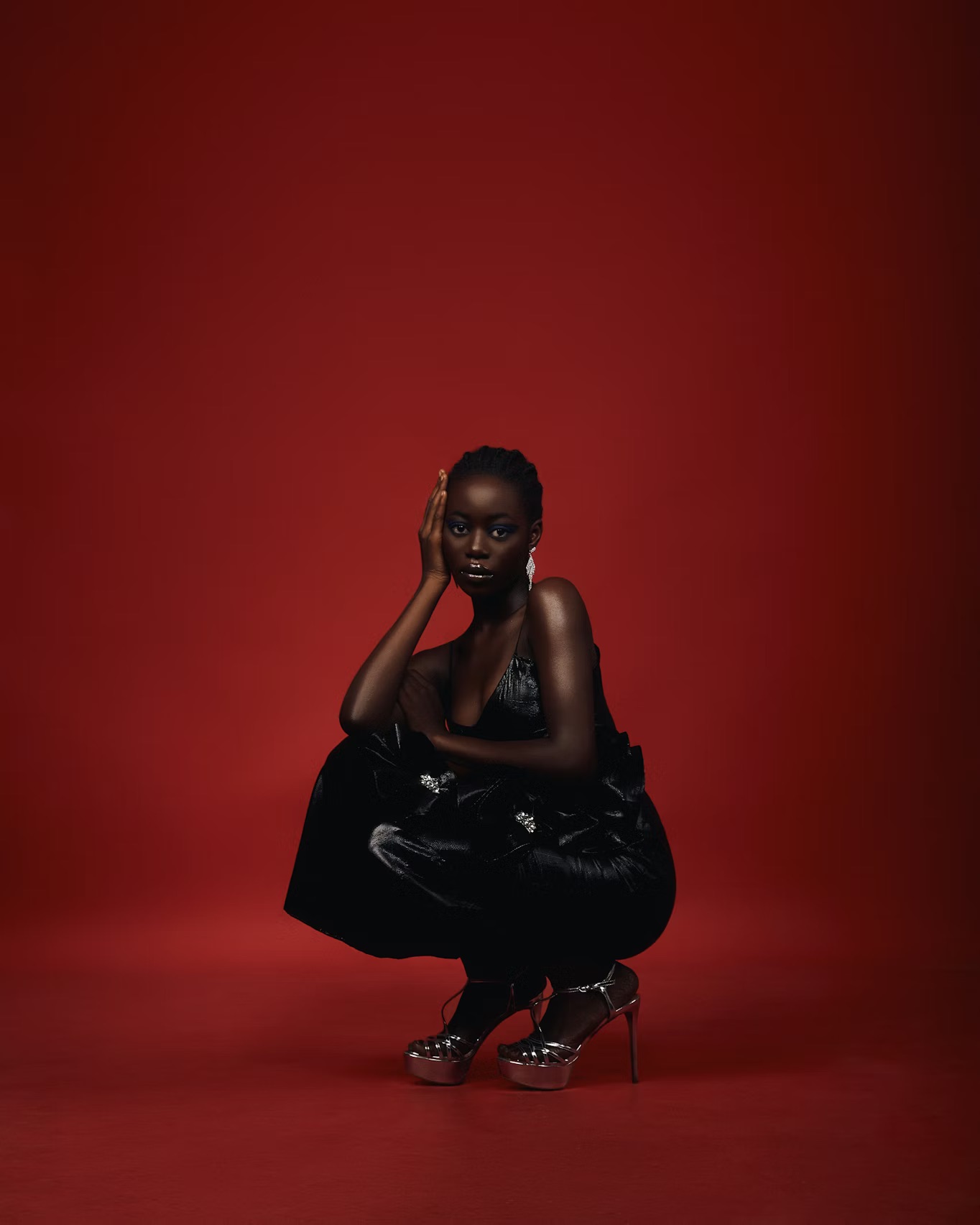

Dark skin often reflects light in striking ways. This gives photographers creative opportunities. Highlights can sculpt the face and enhance its shape. Shine on the skin can look elegant, powerful, or editorial when controlled. The key is intentional placement.
Using a touch of oil or moisturiser can create a glow. Using powder can reduce unwanted shine without making the skin appear flat. Makeup artists who specialise in dark skin tones understand how to balance these elements. Their contributions are invaluable. Photographers should collaborate with them rather than dictate adjustments that might undermine the final look.
Backdrops That Elevate, Not Diminish
The background affects how the viewer sees the skin. Rich jewel tones and deep neutrals often elevate dark skin by enhancing contrast without overwhelming the subject. Very dark backdrops can work when the lighting provides strong separation. Very pale backdrops can work when the exposure is balanced and the lighting is soft.
What matters is intention. If the backdrop and clothing compete with the skin, the final image loses power. When each element supports the subject, the portrait feels cohesive.
Sensitivity Behind the Lens

Technique matters, but sensitivity matters just as much. Dark skin tones have long been underrepresented or misrepresented in fashion photography. Many people with dark skin grew up seeing images that did not reflect them accurately. This history shapes their experience on set.
A respectful photographer acknowledges this context. They communicate openly. They ask about comfort with lighting, makeup choices, and styling. They avoid language that frames dark skin as difficult or challenging. Words carry weight. Saying the skin is beautiful and worth capturing with care builds trust and confidence.
Representation behind the scenes also helps. When the crew includes people who understand the lived experience of the models, the entire environment becomes more inclusive. This leads to better images because the subjects feel seen and respected.
Fashion Context: Celebrating Beauty and Presence
Fashion photography aims to elevate style, mood, and personality. When photographing dark skin, the creative potential is immense. The richness of tone pairs naturally with metallic fabrics, strong silhouettes, bold prints, and sculpted hair. Shadows and light interact in ways that feel cinematic. The result is imagery that stands out in a saturated market.
Many designers are creating collections that celebrate Black identity and culture. When photographers apply proper lighting and sensitivity, they help these collections reach their full visual potential. They also contribute to a more inclusive fashion landscape.
Retouching: A Gentle Hand
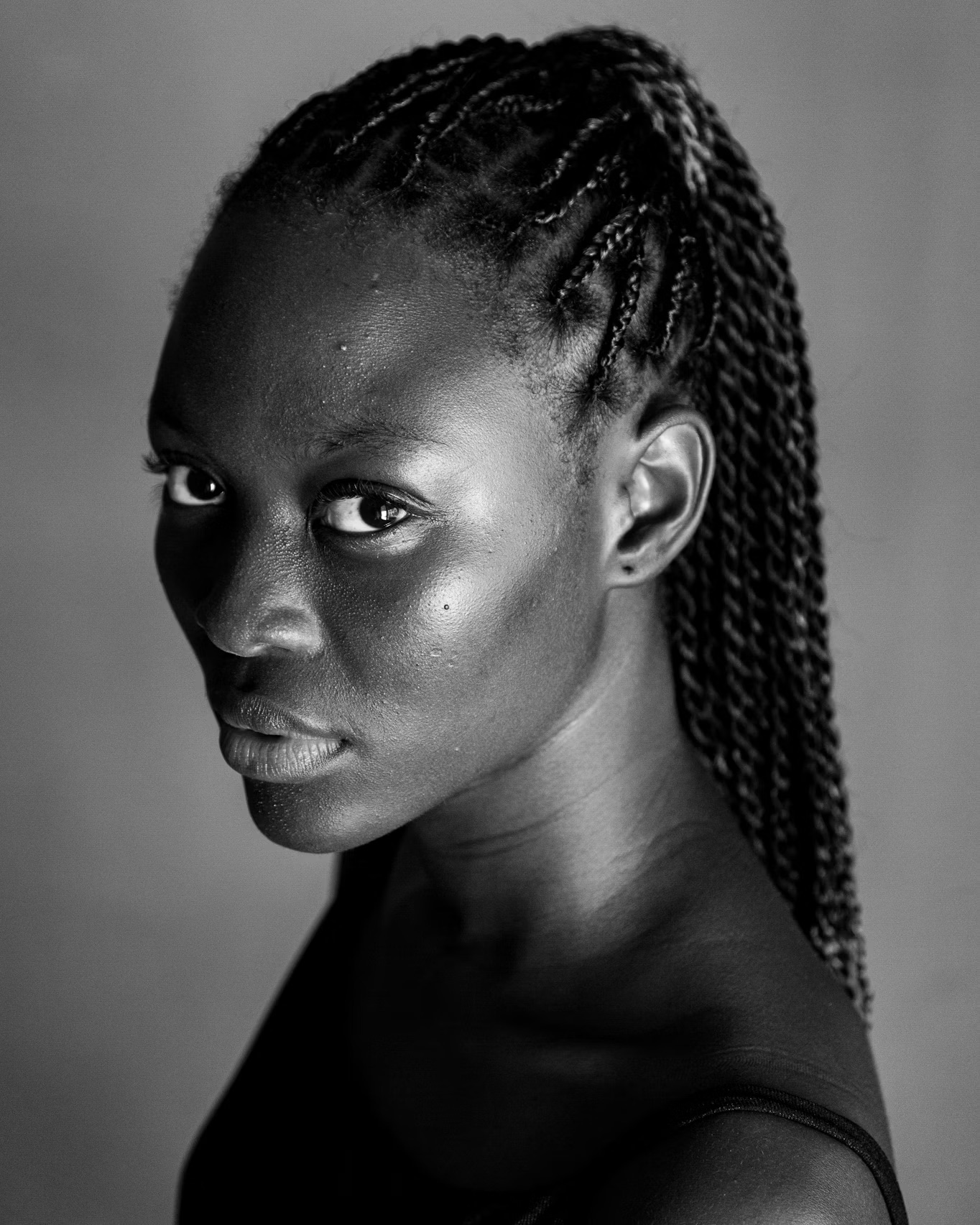
Retouching dark skin should focus on refinement, not alteration. Removing blemishes or stray hairs is fine. Changing the natural tone or texture is harmful. Texture is part of the beauty. Dark skin often looks best when retouching is subtle and respectful.
Avoid brightening the skin in post. Avoid smoothing it to plastic. Maintain the shadows that give the face its shape. Retouching should support the beauty that is already present. Anything else undermines authenticity.
The Bottom Line
Photographing dark skin tones in fashion requires skill, intention, and empathy. The techniques are straightforward once understood. Soft light, balanced exposure, proper white balance, and thoughtful colour choices bring out the richness of the skin. Collaboration with makeup artists and stylists adds polish. Respect for the model builds trust and elevates the final image.
When these elements come together, the results are powerful. Dark skin glows. Features stand out with clarity. Fashion becomes more inclusive. Photography becomes more honest.
The goal is not simply to capture an image. It is to celebrate beauty that has long been overlooked. Photographers who master this responsibility do more than take pictures. They help reshape the industry into one that recognises and honours everyone.































